Design of a Multi-Zone VAV System (the Shorter Way)
Contents
Design of a Multi-Zone VAV System (the Shorter Way)#
In this notebook the example from the previous notebook Design of a Multi-Zone VAV System (the Long Way) is repeated, but now the VAVSystem class will be used, which automates the design procedure of a multi-zone VAV system. This class resides in the module hvac.air_conditioning.vav_system.design. This class can be used for a multi-zone VAV system with cooling and/or heating, having a preheat coil, a cooling coil, and reheat coils at the entrance of the zones. For winter conditions the air is assumed to be totally dry (i.e. only sensible loads are considered).
from hvac import Quantity
from hvac.fluids import HumidAir
from hvac.air_conditioning.vav_system.design import Zone, Season, VAVSystem
from hvac.charts import PsychrometricChart, StatePoint
Q_ = Quantity
Create Zones with Design Data#
The design data of a zone is bundled in a Zone data class. First of all, a zone must have a name. The design data concerning the summer peak design day and the design data concerning the winter peak design day are grouped into two separate instances of the Season class. The design data are the sensible and latent heat load of the zone and the desired state of the zone air. The Season instance with the design data for the summer peak design day is passed through the summer parameter of the Zone class constructor. The Season instance with the design data of the winter peak design day is passed through the winter parameter. Should the VAV system only be used for summer cooling, then the winter parameter can be simply omitted.
Zone A#
zone_A = Zone(
name='zone A',
summer=Season(
Q_sen=Q_(224_844, 'Btu / hr'),
Q_lat=Q_(56_000, 'Btu / hr'),
zone_air=HumidAir(Tdb=Q_(75, 'degF'), RH=Q_(50, 'pct'))
),
winter=Season(
Q_sen=Q_(-143_000, 'Btu / hr'),
Q_lat=Q_(0.0, 'Btu / hr'),
zone_air=HumidAir(Tdb=Q_(75, 'degF'), RH=Q_(0, 'pct'))
)
)
Zone B#
zone_B = Zone(
name='zone B',
summer=Season(
Q_sen=Q_(103_308, 'Btu / hr'),
Q_lat=Q_(20_000, 'Btu / hr'),
zone_air=HumidAir(Tdb=Q_(75, 'degF'), RH=Q_(50, 'pct'))
),
winter=Season(
Q_sen=Q_(49_092, 'Btu / hr'),
Q_lat=Q_(0.0, 'Btu / hr'),
zone_air=HumidAir(Tdb=Q_(75, 'degF'), RH=Q_(0, 'pct'))
)
)
Create VAV System#
Besides the design data of the zones, the global design data about the outdoor air in summer and winter and the design volume flow rate of outdoor air ventilation must be specified.
Outdoor Air Condition on Summer and Winter Design Day
outdoor_air_summer = HumidAir(Tdb=Q_(97, 'degF'), Twb=Q_(76, 'degF'))
outdoor_air_winter = HumidAir(Tdb=Q_(7, 'degF'), RH=Q_(0, 'pct'))
Design Volume Flow Rate of Outdoor Air Ventilation
V_vent = Q_(2400, 'ft ** 3 / min')
Instantiate the VAVSystem Class with the Design Data
vav_system = VAVSystem(
zones=[zone_A, zone_B],
outdoor_air_summer=outdoor_air_summer,
outdoor_air_winter=outdoor_air_winter,
V_vent=V_vent
)
COOLING DESIGN DAY#
After instantiation of the VAVSystem class, call the method design_summer. This method can take a number of keyword arguments:
the maximum allowed temperature difference between the supply air temperature and the zone air temperature in order to enable proper mixing of the supply air with the zone air:
dT_supplythe pressure of the supply air fan:
supply_fan_pressurethe efficiency of the supply air fan:
supply_fan_efficiencyheat gain of the supply duct:
supply_duct_heat_gainthe pressure of the return air fan:
return_fan_pressurethe efficiency of the return air fan:
return_fan_efficiencyheat gain of the return duct:
return_duct_gain
These arguments are not mandatory and can be omitted if they are not known. The supply fan and return fan can only be specified after the volume flow rate of supply and return air have first been determined. As such, the first time the notebook would be executed without values for supply_fan_pressure, supply_fan_efficiency,…
summer_results = vav_system.design_summer(
dT_supply=Q_(20, 'delta_degF'),
supply_fan_pressure=Q_(3, 'inch_H2O_60F'),
supply_fan_efficiency=Q_(60, 'pct')
)
The method design_summer returns a dictionary with the results as shown below. These results are all Quantity objects.
results = {
'cooling coil load': self.summer.cooling_coil.Q,
'sensible cooling coil load': self.summer.cooling_coil.Q_sen,
'latent cooling coil load': self.summer.cooling_coil.Q_lat,
'supply air volume flow rate': self.summer.V_supply,
'return air volume flow rate': self.summer.V_return,
'system supply air temperature': self.summer.supply_air.Tdb,
'system return air temperature': self.summer.return_air.Tdb
}
return results
To quickly show these results in a notebook you may use the (static) method show_results_markdown of the VAVSystem instance. For this you need to pass the returned results from design_summer together with a dictionary units containing the units in which you want the results to be displayed and the number of decimals behind the decimal point, as is demonstrated below.
ja.display_list(
vav_system.show_results_markdown(
summer_results,
units={
'Q': ('Btu / hr', 0),
'V': ('ft ** 3 / min', 0),
'K': ('degF', 1)
}
)
)
- cooling coil load: -545782 Btu/h
- sensible cooling coil load: -411416 Btu/h
- latent cooling coil load: -134114 Btu/h
- supply air volume flow rate: 14750 ft³/min
- return air volume flow rate: 15350 ft³/min
- system supply air temperature: 55.0 °F
- system return air temperature: 75.0 °F
Psychrometric Chart#
The data attributes of the summer (and winter) attribute of the VAVSystem class are all accesible. The code below shows the __init__ method of the Summer subclass of the VAVSystem class with all its data attributes. The names of the data attributes should speak for themselves.
def __init__(self, outdoor_air: HumidAir, V_vent: Quantity, system: 'VAVSystem'):
self.outdoor_air = outdoor_air
self.m_vent = V_vent * outdoor_air.rho
self.system = system # reference to the instance of the `VAVSystem` parent class
self.T_supply: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'degC')
self.supply_air: Optional[HumidAir] = None
self.m_supply: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'kg /s')
self.V_supply: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'kg /s')
self.T_cold: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'degC')
self.cooled_air: Optional[HumidAir] = None
self.m_return: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'kg /s')
self.V_return: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'kg /s')
self.return_air: Optional[HumidAir] = None
self.recirculated_air: Optional[HumidAir] = None
self.mixed_air: Optional[HumidAir] = None
self.cooling_coil: Optional[AirConditioningProcess] = None
self.m_supply_part_load: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'kg /s')
self.V_supply_part_load: Quantity = Q_(float('nan'), 'kg /s')
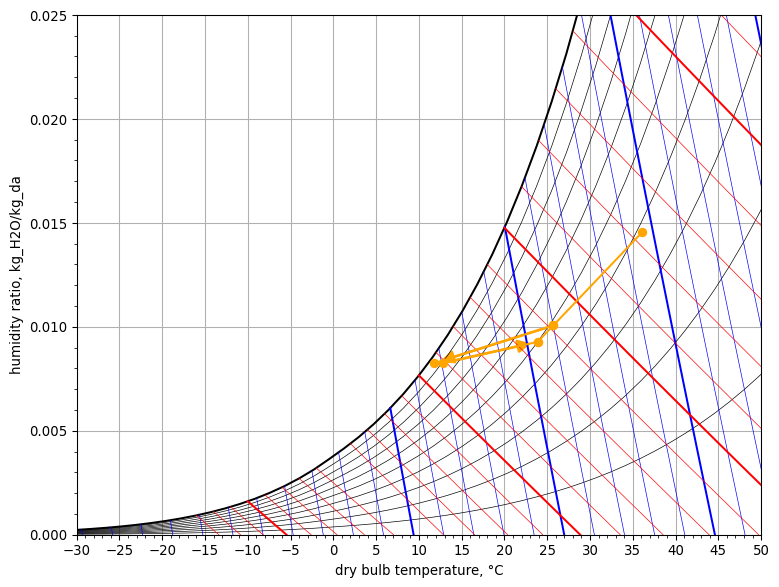
Taking the appropriate data attributes, it is possible to draw the pyschrometric chart and plot the air conditioning processes in the VAV system.
chart = PsychrometricChart(fig_size=(8, 6))
chart.plot_process(
'mixing_chamber',
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.outdoor_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.outdoor_air.W),
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.return_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.return_air.W),
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.mixed_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.mixed_air.W)
)
chart.plot_process(
'cooling coil',
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.mixed_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.mixed_air.W),
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.cooled_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.cooled_air.W)
)
# chart.plot_process(
# 'supply fan',
# StatePoint(vav_system.summer.cooled_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.cooled_air.W),
# StatePoint(vav_system.summer.supply_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.supply_air.W)
# )
chart.plot_process(
'zones',
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.supply_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.supply_air.W),
StatePoint(vav_system.summer.return_air.Tdb, vav_system.summer.return_air.W)
)
chart.show()
Zone Info#
The zones, instances of the Zone class, are kept in a list inside the VAVSystem class. A Zone object has two members summer and winter that refer to an instance of the Season dataclass that contains the design data for the zone. From the implementation of the Season dataclass, it can be seen which data attributes are available. Again the names of the data attributes should speak for themselves.
@dataclass
class Season:
Q_sen: Quantity
Q_lat: Quantity
zone_air: HumidAir
m_exhaust: Quantity = Q_(0.0, 'kg / s')
m_supply: Optional[Quantity] = field(init=False, default=Q_(float('nan'), 'kg / s'))
supply_air: Optional[HumidAir] = field(init=False, default=None)
return_air: Optional[HumidAir] = field(init=False, default=None)
@property
def m_return(self) -> Quantity:
return self.m_supply - self.m_exhaust
@property
def V_supply(self) -> Quantity:
return self.m_supply * self.supply_air.v
@dataclass
class Zone:
name: str
summer: Optional[Season] = None
winter: Optional[Season] = None
reheat_coil: Optional[AirConditioningProcess] = field(init=False, default=None)
Notes
Attribute
m_exhaustmay refer to local exhaust of air in a zone.To get at the resulting air state (in particular air humidity) of a zone, the
return_airattribute should be used, as thezone_airattribute is used to specify the desired zone air state when instantiating the zone.
ja.display_list([
f"return air at {zone.name}: <b>{zone.summer.return_air.Tdb.to('degF'):~P.1f} TDB, "
f"{zone.summer.return_air.RH.to('pct'):~P.0f} RH</b>, "
f"supply air volume flow rate: <b>{zone.summer.V_supply.to('ft ** 3 / min'):~P.0f}</b>"
for zone in vav_system.zones
])
- return air at zone A: 75.0 °F TDB, 50 % RH, supply air volume flow rate: 10106 ft³/min
- return air at zone B: 75.0 °F TDB, 49 % RH, supply air volume flow rate: 4644 ft³/min
HEATING DESIGN DAY#
winter_results = vav_system.design_winter(
T_supply_max=Q_(105, 'degF'),
supply_fan_pressure=Q_(3.0, 'inch_H2O_60F'),
supply_fan_efficiency=Q_(60.0, 'pct')
)
ja.display_list(
vav_system.show_results_markdown(
winter_results,
units={
'Q': ('Btu / hr', 0),
'V': ('ft ** 3 / min', 0),
'K': ('degF', 1)
}
)
)
- preheat coil peak load: 137878 Btu/h
- preheat coil load: 29050 Btu/h
- total reheat coil load: 249846 Btu/h
- cooling coil load: 0 Btu/h
- sensible cooling coil load: 0 Btu/h
- latent cooling coil load: 0 Btu/h
- supply air volume flow rate: 8805 ft³/min
- return air volume flow rate: 9075 ft³/min
- system supply air temperature: 59.2 °F
- system return air temperature: 75.0 °F
ja.display_list([
f"{zone.name}: supply air temperature = <b>{zone.winter.supply_air.Tdb.to('degF'):~P.1f}</b>, "
f"reheat load = <b>{zone.reheat_coil.Q_sen.to('Btu / hr'):~P.0f}</b>, "
f"supply air volume flow rate = <b>{zone.winter.V_supply.to('ft ** 3 / min'):~P.0f}</b>"
for zone in vav_system.zones
])
- zone A: supply air temperature = 96.2 °F, reheat load = 249846 Btu/h, supply air volume flow rate = 6465 ft³/min
- zone B: supply air temperature = 59.2 °F, reheat load = 0 Btu/h, supply air volume flow rate = 2772 ft³/min

